UV Resistance Basics By The Numbers

Yellowing fixtures cheapen your property's appearance. You can prevent this costly problem with a numbers-based strategy. Understanding UV resistance basics transforms your purchasing decisions from a guess into a predictable investment.
Key Metrics to Master:
- The 1,000-hour QUV test
- Delta E (dE) color values
- 99% UV-blocking films
These numbers are your best defense against sun damage. They ensure your fixtures remain pristine for years.
Core UV Resistance Basics

Understanding a few UV resistance basics helps you make smarter purchasing choices. Sunlight contains invisible ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This radiation is the primary cause of yellowing and material breakdown in your fixtures. You can protect your investment by understanding how this damage happens and how to stop it.
How UV Radiation Causes Yellowing
UV radiation from the sun, especially UVA and UVB rays, triggers a damaging chemical process. This process is called photo-oxidative degradation. It is a cumulative and irreversible reaction that weakens your fixtures over time.
The Degradation Process 🔬
- UV energy strikes the surface of a material.
- This energy breaks the long polymer chains that give the material its strength.
- The broken chains produce unstable particles called free radicals.
- These free radicals start a chain reaction, causing more damage.
- This ongoing reaction leads to visible yellowing and makes the material brittle.
Three Methods of UV Protection
Manufacturers use three primary methods to defend materials against UV degradation. Knowing these methods helps you select fixtures built for longevity.
-
Inherently Stable Materials: The best defense is a strong foundation. Some materials naturally resist UV damage. Plastics like acrylic, polycarbonate (PC), and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) show excellent stability even after years of sun exposure. You should prioritize these materials for high-exposure areas.
-
UV Absorbers: Think of these additives as a microscopic shield. Manufacturers mix them into plastics and coatings. UV absorbers attract harmful UV radiation, convert it into low-level heat, and safely release it. This protects the polymer underneath from breaking down.
-
Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers (HALS): These additives work like an internal repair crew. When UV radiation creates damaging free radicals, HALS trap and neutralize them. This action stops the destructive chain reaction before it can cause yellowing or embrittlement. HALS are also regenerative, allowing them to work for a long time.
Understanding UV Resistance Metrics
You can move beyond guesswork by using standard industry metrics. These numbers provide clear, comparable data on how well a material will perform. Mastering them is a core part of understanding UV resistance basics.
The QUV Test: A 1,000-Hour Benchmark
The QUV accelerated weathering test is your most reliable tool for predicting durability. This test puts material samples inside a chamber that simulates years of sun and moisture damage in just weeks. It follows strict industry standards, like ASTM G154, using a cycle of intense UV light, heat, and condensation to mimic outdoor exposure.
While there is no perfect conversion, 1,000 hours in a QUV chamber can equal anywhere from six months to two years of real-world sun exposure. This makes it an excellent comparative test.
The Hospitality Benchmark 🏆 For fixtures in hotels and commercial properties, you should look for products that pass a 1,000-hour QUV test without significant damage or color change. This number signals a durable, long-lasting investment.
Delta E: The Color Change Number
Delta E (often written as dE) is the standard metric for measuring color change. After a material completes a QUV test, technicians measure its color and compare it to the original. The difference between the two is expressed as a single number: the Delta E value. This number tells you exactly how much a fixture has yellowed or faded.
You can interpret the Delta E scale easily.
| Delta E (dE) Value | Perceptible Color Change |
|---|---|
| Below 1.0 | Not visible to the human eye |
| 1.0 – 2.0 | Only visible to a trained eye |
| 3.0 or more | Clearly noticeable change |
When you specify fixtures, you should demand a low Delta E value. Ask your suppliers for products with a dE of less than 3.0 after 1,000 hours of QUV testing. This ensures your fixtures will maintain their original color for years.
Choosing Materials by the Numbers
You can select the right fixtures for any location by using QUV test data. Materials fall into clear performance tiers based on their test hours. This knowledge is a fundamental part of UV resistance basics. It helps you match the material to the environment, preventing premature failure and protecting your budget.
Top Performers: 1,500+ QUV Hours
Top-performing materials offer maximum protection in the most demanding environments. These materials can withstand 1,500 hours or more in a QUV chamber with minimal change. You should specify them for high-value fixtures with constant, direct sun exposure. They represent the ultimate long-term investment.
When to Choose Top Performers ☀️ Use these materials for critical, high-exposure applications. Your investment will be protected for years to come.
- Outdoor signage and wayfinding
- Poolside furniture and fixtures
- Rooftop terrace elements
- Coastal property exteriors
Common top performers include:
| Material | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Acrylic (PMMA) | Exceptional optical clarity and natural UV stability. |
| Fluoropolymers (e.g., PVDF) | Superior chemical and UV resistance, often used in coatings. |
| High-Grade Stabilized PC | Polycarbonate with advanced UV protection packages. |
Industry Standard: 1,000+ QUV Hours
Materials in this category provide the perfect balance of performance and cost for most commercial applications. They meet the 1,000-hour QUV benchmark, ensuring fixtures resist yellowing and degradation for years in typical hotel settings. You should make this your default specification for most fixture purchases.
The Smart Choice for Hospitality ✅ For the majority of your property's needs, from guest room lighting to lobby fixtures, demanding a 1,000+ hour QUV rating is your most effective strategy. It guarantees durability without overspending on materials designed for extreme conditions.
These reliable materials often include:
- UV-Stabilized Polycarbonate (PC)
- UV-Stabilized High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Specialty Polyesters
- Fixtures with high-performance UV-resistant coatings
High-Risk Materials: Under 500 QUV Hours
You must identify and avoid high-risk materials in any area with sun exposure. These materials often fail in under 500 hours of QUV testing. They are not designed for UV stability and will quickly yellow, crack, or become brittle. Using them for the wrong application leads to costly and frequent replacements.
Some materials show extreme weakness under UV testing. For example, Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) can lose nearly half of its tensile strength after just 50 hours of exposure. Other plastics, like certain polyethylene films, show a 40% drop in molecular weight after about 500 hours of simulated exposure. This data reveals a rapid breakdown process.
Warning: Avoid for Sun-Exposed Areas 🚫 Never use the following materials for fixtures that receive direct or indirect sunlight. Their low cost is deceptive, as they will fail quickly.
- General-Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS)
- Non-stabilized Polypropylene (PP)
- Standard Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS)
These materials may be acceptable only for interior spaces completely shielded from windows and sunlight.
Protective Measures and Key Metrics
Beyond choosing the right materials, you can add layers of defense to protect your property. These proactive measures shield your fixtures from UV damage. They also offer significant returns by lowering energy and maintenance costs.
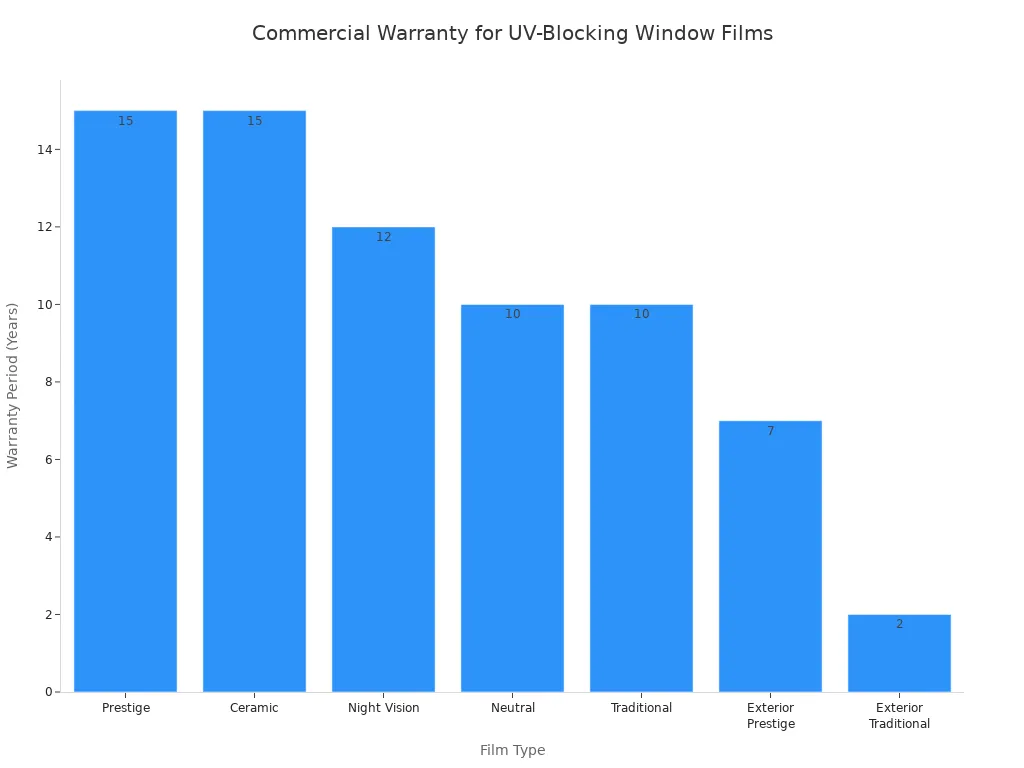
Window Films: 99% UV Blockage
You can stop UV radiation before it even enters a room. Professional-grade window films block over 99% of harmful UVA and UVB rays. This simple upgrade provides a powerful shield for your furniture, flooring, and fixtures. It dramatically slows down the yellowing and fading process. Modern films like ceramic and Low-E (Low Emissivity) options offer excellent protection without changing the look of your windows.
Installing these films is a smart financial decision. The initial cost, typically between $5 and $14 per square foot, delivers a strong return on investment. You can often recover the cost in just 2 to 5 years through energy savings alone. The films reduce the load on your HVAC system, lowering utility bills. They also extend the life of your interior assets, reducing the need for costly refurbishments.
Long-Term Reliability 🛡️ Professional window film installations are built to last. Many products come with commercial warranties that reflect their durability, giving you peace of mind for over a decade.
LED Lighting: The 3,000K Rule
Your choice of lighting also plays a role in protecting your fixtures. While modern LEDs emit very little UV radiation compared to older bulbs, it is still a factor for long-term exposure. You can minimize this risk by following a simple guideline.
The 3,000K Rule💡 Choose LED lights with a color temperature of 3,000 Kelvin (K) or lower for interior spaces.
This color temperature produces a warm, inviting light that is ideal for hospitality environments. More importantly, LEDs in this range emit virtually no UV radiation. This small detail contributes to your overall strategy for preserving fixtures. Investing in quality materials and lighting reduces future maintenance costs. It ensures your furniture, fixtures, and equipment remain functional and attractive for years, protecting your investment.
You can protect your property and enhance your brand image with a data-driven approach. Following these UV resistance basics transforms purchasing into a predictable investment strategy. This leads to measurable cost savings and extends the life of your fixtures.
Your 3-Step Procurement Checklist ✅
- Specify Performance: Demand fixtures rated for 1,000+ QUV hours with a Delta E (dE) value under 3.0.
- Block the Source: Install window films that block over 99% of UV radiation.
- Choose Smart Materials: Select inherently stable materials like acrylic for high-sunlight areas.
FAQ
What is the most important number to remember?
You should focus on two key metrics for fixture durability. These numbers provide a clear standard for performance and protect your investment from sun damage.
Key Specifications 🎯
- QUV Test: 1,000+ hours
- Delta E (dE): Under 3.0
Do 1,000 QUV hours equal a set number of years?
No, the QUV test does not convert perfectly to years. It is a comparative tool. It helps you understand how one material will perform against another under identical, harsh conditions. A higher QUV rating always means better durability.
Are UV-resistant materials worth the extra cost?
Yes, they provide excellent long-term value. You pay a small premium upfront to avoid frequent and costly replacements later. This choice protects your budget and brand image.
| Investment | Result |
|---|---|
| Low Initial Cost | Frequent Replacement |
| Higher Initial Cost | Long-Term Durability |
Do I need UV protection for indoor fixtures?
Yes, you do. Sunlight streams through windows and can damage indoor items. You can protect your interior fixtures from this damage.
☀️ Use 99% UV-blocking window films. 💡 Choose LED lights at 3,000K or lower.