What is Optical Clarity (Light Transmittance)?

One-Sentence Definition
Optical clarity (light transmittance) is the measure of how much visible light passes through a transparent material, indicating its transparency and visual quality.
Detailed Explanation
Optical clarity, often quantified as light transmittance, describes the ability of a material—such as acrylic, glass, or polycarbonate—to allow visible light to pass through with minimal distortion or scattering. High optical clarity means the material appears clear and objects behind it are seen sharply and accurately. This property is critical in applications where true color, detail, and brightness are essential, such as display cases, protective covers, and lighting fixtures.
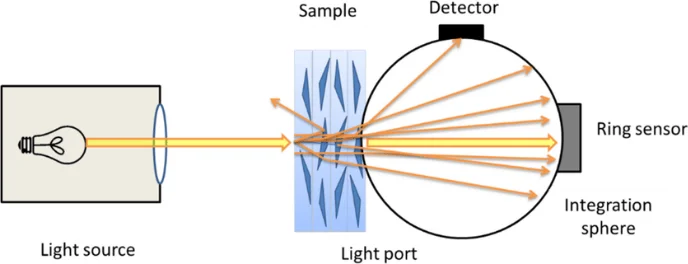
Light transmittance is typically expressed as a percentage, representing the ratio of transmitted light to incident light. For example, a transmittance of 92% means that 92% of the incoming visible light passes through the material. International standards like ISO 13468-1 and ASTM D1003 specify how to measure this property using photometric equipment and controlled lighting conditions.
Key Components
- Total Luminous Transmittance: The percentage of visible light that passes through the material, measured under standardized conditions. High-quality acrylic typically achieves values around 92%.
- Haze: The degree to which light is scattered as it passes through the material. Low haze (usually <2%) is essential for pristine clarity. Even with high transmittance, high haze can make a material look cloudy. (Learn more about haze)
- Refractive Index: Indicates how much light bends as it enters the material. Uniform refractive index (acrylic ~1.49) ensures minimal distortion.
- Surface Quality: Scratches, roughness, or impurities can reduce clarity by increasing light scattering.
Real-World Applications
Optical clarity is a defining feature for materials used in:
- Display Stands and Showcases: High transmittance and low haze ensure products are presented with true color and detail.
- Protective Covers and Shields: Clear acrylic covers for electronics or museum artifacts rely on high optical clarity for visibility and protection.
- Lighting Fixtures: Maximizing light output and uniformity in luminaires and architectural lighting.
- Medical and Laboratory Equipment: Where accurate visual inspection is critical.
Acrylic is widely chosen for these applications due to its excellent optical clarity (92% transmittance, <2% haze), lightweight nature, and durability. Thickness, manufacturing process, and surface treatment can all influence the final clarity.
Related Concepts
- Transparency: A qualitative description of how clearly objects can be seen through a material.
- Transmittance: The quantitative measure of light passing through a material.
- Haze: The percentage of light scattered, affecting visual sharpness.
- Refractive Index: Governs how light bends in the material, impacting clarity and distortion.
- Gloss: The surface’s ability to reflect light specularly, contributing to perceived shine.
- Opacity: The degree to which a material blocks light.
Visual Aids
Further Reading
- ISO 13468-1: Plastics – Determination of the Total Luminous Transmittance of Transparent Materials
- Haze: How does it affect optical clarity of plastics?
- Measuring Transparency, Lensing, And Optical Clarity
By understanding and specifying optical clarity and light transmittance, manufacturers and designers can ensure their products meet the highest standards of visual performance and user experience.