Cost drivers explained shocking screen price gaps

The high cost of a smartphone repair often surprises consumers. This sticker shock is a common experience in the current market. The final price of a repair is a mix of many factors.
A flagship smartphone screen repair can cost over $300. This specific repair is expensive because of complex parts. 📱
The smartphone repair market reflects this reality. High repair demand in this market influences the final repair price. These cost drivers explained the price gap. A modern display is complex. Advances in repair technology also shape the repair. The entire smartphone repair market and the broader market for a repair contribute to the final price of a repair.
Core technology: OLED vs. LCD

The fundamental technology inside a screen is the biggest factor in its price. A smartphone uses one of two main types: OLED or LCD. The choice between them directly impacts the device's cost and the bill for a future repair. Understanding this difference is the first step to demystifying screen prices.
OLED displays
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. In an OLED display, each tiny pixel produces its own light. This individual control has a huge impact on image quality. When a pixel needs to be black, it simply turns off completely.
Deep Blacks, Vibrant Colors OLED screens can achieve a contrast ratio of 1,000,000:1. This means they show true, deep blacks next to bright, vibrant colors. This capability delivers stunning visual performance and superior image quality. A difficult screen repair often involves this tech.
This advanced technology is complex to manufacture. The higher production cost translates to a more expensive smartphone. It also means a screen repair will be more costly. The delicate nature of OLED panels makes the repair process more difficult. Many top brands choose OLED for their flagship models.
- Apple uses OLED screens in its iPhone Pro models.
- Samsung features its own Dynamic AMOLED screens in the Galaxy S series.
- Google includes advanced LTPO AMOLED displays in its Pixel smartphone family.
The market is shifting heavily toward this premium technology. Data shows that OLED screens now dominate new smartphone shipments, making this expensive technology the new standard. A repair for these popular devices will reflect the screen's high initial cost. The complexity of an OLED repair adds to the final price.

| Display Type | Shipments (2024) | Year-over-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
| AMOLED | 784 million units | +26% |
| TFT LCD | 761 million units | -8% |
The prevalence of OLEDs means a higher average cost for a screen repair across the industry.
LCD displays
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display. Unlike OLEDs, LCD screens use a single backlight to illuminate all the pixels at once. The pixels act like tiny shutters, blocking or letting light pass through to create an image. This method is simpler and cheaper to produce.
The main drawback is light control. Since the backlight is always on, LCDs cannot achieve true black. Some light always leaks through the pixels, making dark areas appear grayish. This results in lower contrast and less vibrant color quality compared to OLEDs.
However, the lower manufacturing cost is a significant advantage. A smartphone with an LCD screen is generally more affordable. Consequently, an LCD repair is also much cheaper. The parts are less expensive and the repair process is often simpler. While high-end phones have moved away from LCDs, this technology is still common in budget-friendly models, making their repair more accessible. The lower cost of an LCD repair makes it an attractive option for many consumers.
Manufacturing and design complexity

Beyond the core technology, the specific design and manufacturing processes of a screen add significant costs. Intricate details like pixel density, refresh rate, and panel shape require precision engineering. These complexities directly increase the price of a smartphone and the cost of a screen repair.
Resolution and pixel density (PPI)
A screen's resolution refers to the number of pixels it contains. Pixel density, measured in Pixels Per Inch (PPI), describes how tightly those pixels are packed. A higher PPI creates a sharper, clearer image. However, achieving high pixel density is a difficult manufacturing challenge.
The Concept of "Yield" In manufacturing, "yield" is the percentage of non-defective products from a production run. Packing more pixels into a small space increases the chance of defects. A single dead pixel can make an entire screen unusable. As a result, high-resolution screens have lower yields. This means manufacturers must produce more screens to get one perfect unit, driving up the cost for each successful display. A repair involving a high-PPI screen reflects this expensive reality.
High refresh rates (120Hz+)
Modern screens offer high refresh rates, like 120Hz or higher. This number indicates how many times the screen updates per second. A higher rate provides smoother scrolling and better gaming performance. Technologies like LTPO (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Oxide) allow a smartphone to adjust its refresh rate dynamically, saving battery life. This advanced capability comes at a high price. The manufacturing process is very complex and affects the cost of a repair.
Implementing this technology presents several challenges:
- Complex Production: It requires combining different technologies and using specialized equipment.
- Difficult Design: Engineers work hard to balance power use, screen performance, and production costs.
- High Investment: Factories need significant upgrades to produce these advanced screens.
- Lower Yields: The complexity leads to more errors, increasing the cost per screen and making a repair more expensive.
This technology improves the user experience with better speed and responsiveness, but it also makes the initial device and any future repair more costly.
Curved vs. flat panel design
The shape of the screen panel is another major cost driver. Curved or "waterfall" screens create an immersive, borderless look. This premium design requires a far more complicated manufacturing process than a simple flat panel. The higher difficulty increases the price of the smartphone and the cost of a repair.
Making a curved screen involves specialized machinery. For example, machines like the ND-1311KL perform high-precision cutting on glass, while others like the TBK-408F handle the difficult task of laminating layers onto a curved surface. This process has a higher defect rate. Bending glass and flexible display components without causing damage is extremely difficult. The higher rate of failure during production makes each successful curved screen more valuable. This value is passed on to the consumer, making the initial purchase and any potential repair significantly more expensive than a repair for a flat-screen device. The final image quality is high, but the repair cost matches this premium quality.
Integrated features in the modern smartphone
A modern smartphone screen is more than just a display. It is a complex assembly of integrated technologies. These features, from security sensors to durable glass, add significant value and cost. This complexity makes a screen repair more difficult and expensive.
In-display fingerprint sensors
Many devices now place the fingerprint sensor directly under the screen. This feature comes in two main types: optical and ultrasonic. Ultrasonic sensors are more expensive and are usually found in premium flagship smartphone models. Optical sensors are cheaper, making them common in mid-range devices. The type of sensor affects the cost of a screen repair. A repair for a screen with an ultrasonic sensor is typically more costly due to the advanced technology involved.
| Feature | Optical Sensors | Ultrasonic Sensors |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Cheaper to manufacture | More expensive to manufacture |
| Performance | Less accurate, noticeable lag | More accurate, faster speed |
| Security | Easier to fool with a 2D image | More secure with a 3D scan |
The higher performance and security of ultrasonic sensors justify their cost in a high-end smartphone, but this also increases the price of a potential repair.
Proprietary glass and coatings
Manufacturers use special, branded glass to protect screens from scratches and drops. These materials are not ordinary glass. Companies invest heavily in research to develop them.
- Corning's Gorilla Glass Victus is a popular choice for many Android devices.
- Apple's Ceramic Shield, used in recent iPhones, embeds ceramic crystals into the glass.
This advanced protection comes from expensive development and licensing fees. While this glass improves durability, it also raises the initial cost of the smartphone. A repair that requires replacing this specialized glass will reflect its high material cost and quality. The difficult replacement process also adds to the final repair bill.
Advanced digitizers and touch layers
The digitizer is the touch-sensitive layer of the screen. It converts your finger or stylus movements into digital signals. Basic digitizers handle simple taps and swipes. Advanced digitizers, however, offer much more. They can detect varying levels of pressure, which is essential for tasks like digital drawing.
Technologies like Electro-Magnetic Resonance (EMR) provide a realistic pen-on-paper experience. This high-quality precision is crucial for creative and technical work. Integrating such a sensitive component into the display assembly is a complex engineering task. This complexity increases the screen's production cost, which directly impacts the price of the smartphone and any future screen repair. A repair on a device with an advanced digitizer requires careful handling to preserve its delicate functionality.
More cost drivers explained: Market and brand factors
The price of a smartphone screen goes beyond its physical parts. The final cost you pay is also shaped by invisible forces. These market and brand factors are important cost drivers explained here. A company's research spending, brand image, and the competitive market all add to the price of a new smartphone and a future repair. The smartphone repair market is heavily influenced by these elements.
Research & Development (R&D) costs
Companies invest huge sums of money to invent the next great screen technology. This research and development (R&D) is a major expense. For example, Samsung developed the first touch-integrated OLED display, a big step forward. These innovations require billions of dollars. This spending is a key part of the cost drivers explained in the final price.
| Company | Annual R&D Investment |
|---|---|
| Samsung Display | USD 4 Billion |
| LG Display | USD 3 Billion |
| BOE Technology | USD 2.5 Billion |
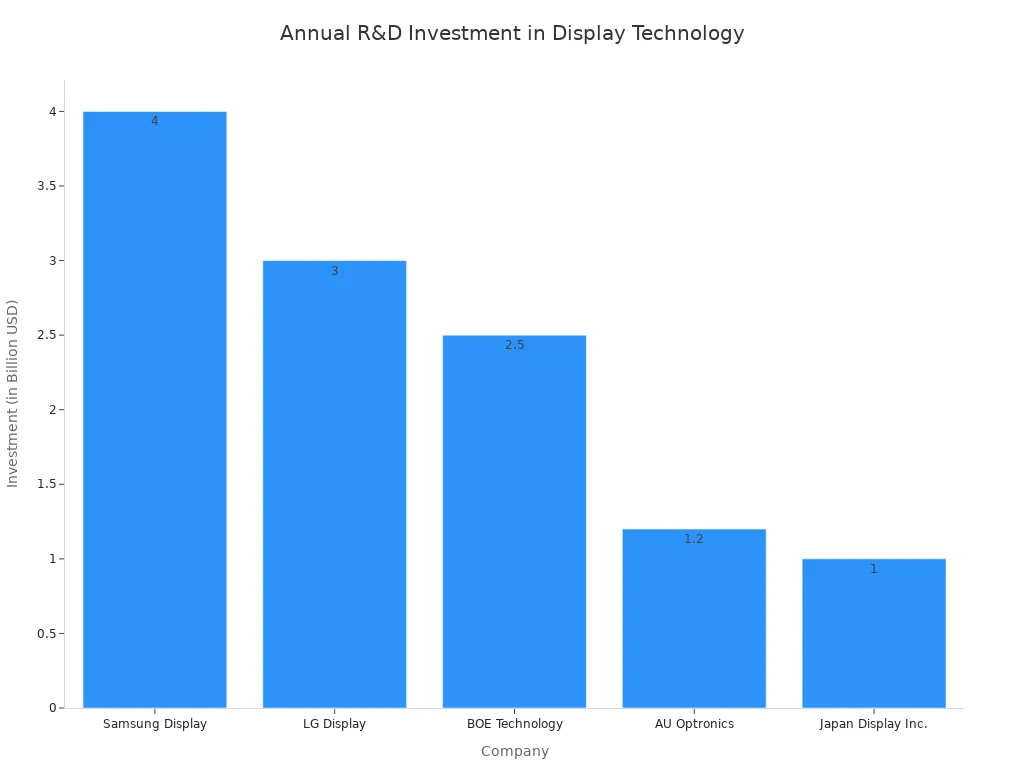
Companies spread this R&D cost over the product's life. A smartphone has a short life, often just three years. The company adds a piece of the R&D expense to each smartphone it sells. This makes the device and any screen repair more expensive. The high demand for new features fuels this cycle in the smartphone repair market.
Branding and marketing influence
A brand's name and reputation add to the price. Premium brands like Apple and Samsung charge more because of their perceived value. This affects both the smartphone price and the repair cost. Apple uses proprietary parts, making an iPhone repair expensive. Samsung's curved screens also require a specialized, costly repair. The smartphone repair market sees high demand for these top-tier brands.
The brand of a smartphone significantly impacts its repair price. While a Samsung device might seem like a good deal initially, its high repair cost can make it less economical in the long run compared to an iPhone, where repair options can become cheaper over time.
The supply of parts in the smartphone repair market also differs. Apple's repair parts may become more available over time, lowering the price of a repair. Samsung often restricts its screen supply, keeping repair prices high. This creates a different market dynamic for each brand's repair services.
Competition and retail pricing
Competition between screen makers also affects prices. The display market has dominant players like Samsung and rising competitors like BOE. When more companies compete, they may lower prices to win business from smartphone makers. This competition can lead to a less expensive screen repair for consumers. A competitive market helps control prices across the smartphone repair market. The high demand for cheaper alternatives pushes this competition. The manufacturer's suggested retail price (MSRP) also sets a baseline for what you pay. However, the real price in the market for a repair can change based on supply and demand. A healthy market with many suppliers benefits everyone, from the phone maker to the person needing a repair.
The final cost of a smartphone repair is complex. These cost drivers explained the price. The smartphone repair market is a large market. High demand in this market affects every repair. The smartphone repair market is a dynamic market. The market for a repair is growing. The market for a smartphone repair is competitive. The market for a repair is influenced by supply. The smartphone repair market sees high demand for a repair. A repair for a smartphone is expensive. A repair is a common need. A repair is a difficult process. A repair is a necessary service.
Understanding these factors empowers consumers. People can make smarter choices about their next smartphone purchase or repair, knowing the value behind the price.
FAQ
Why is an OLED screen repair so expensive?
OLED technology is complex and costly to produce. The delicate nature of the panels makes the repair process difficult. A professional repair requires specialized tools and skills. This complexity increases the final cost for a screen repair, making it a premium service.
Does a small crack require a full screen repair?
Yes, a small crack often needs a full screen repair. Modern screens fuse the glass, touch layer, and display into one unit. Separating them is not possible for a simple repair. Therefore, the entire assembly needs replacement for any damage, making the repair extensive.
How does a brand affect the cost of a repair?
Premium brands use proprietary parts and control the supply chain. This limits part availability and keeps prices high for a screen repair. A brand's reputation for quality also adds to the perceived value, influencing the overall price of a phone repair.
Is a third-party repair a cheaper option?
A third-party repair can be cheaper. These shops may use non-original parts to lower the cost. However, the quality might not match the original manufacturer's standards. Consumers weigh cost against quality when choosing a repair service for their device.