Battery Maintenance Best Practices for Storage and Use

You want your battery to last longer. Good news—simple steps can make a big difference. Battery Maintenance saves you money and keeps your devices working when you need them most. Follow this battery care guide, and you’ll help the planet by cutting down on waste. Small changes matter!
Battery Maintenance Basics
Why Battery Maintenance Matters
You might wonder why battery maintenance is so important. When you take care of your battery, you help it last longer and work better. Battery manufacturers say that simple steps like recharging batteries regularly, storing them in cool, dry places, and following the right charging habits can make a big difference. If you use lithium-ion batteries, these habits are even more important. Good lithium battery maintenance means you avoid problems like overheating or swelling.
Routine maintenance helps you spot damage early. You should check your battery for leaks or dirt. Clean the terminals and keep the cables tight. These steps protect your devices and keep you safe. When you follow these habits, you extend your lithium battery lifespan and save money. You also help the environment by reducing waste.
Tip: For lithium-ion battery health, avoid letting your battery stay at 0% or 100% for long. Try to keep it between 20% and 80% most of the time.
Common Battery Issues
You may face some common problems with lithium-ion batteries in your devices. Here’s a quick look at what can go wrong:
Issue | Cause | What You Notice |
|---|---|---|
Battery drains fast | Old battery, background apps, high usage | Power drops quickly |
Overheating | Faulty charger, heavy use, poor airflow | Device feels hot |
Only works when plugged in | Dead cells, damaged connectors | Shuts off when unplugged |
Swelling | Internal damage, overcharging | Battery or device looks puffy |
Sudden shutdowns | Calibration issues, hardware faults | Turns off without warning |
If you see these issues, routine maintenance can help. Managing temperature, using the right charger, and storing your battery well all support a longer lithium-ion battery lifespan. These habits protect your lithium-ion battery and keep your devices running smoothly.
Battery Lifespan Factors
Age and Chemistry
You might notice your battery does not last as long as it did when it was new. This happens because batteries age over time, even if you do not use them much. Calendar aging means the battery loses capacity just by sitting around. Cycle aging happens each time you use and recharge your battery. Both types of aging cause the battery to hold less energy and work for shorter periods.
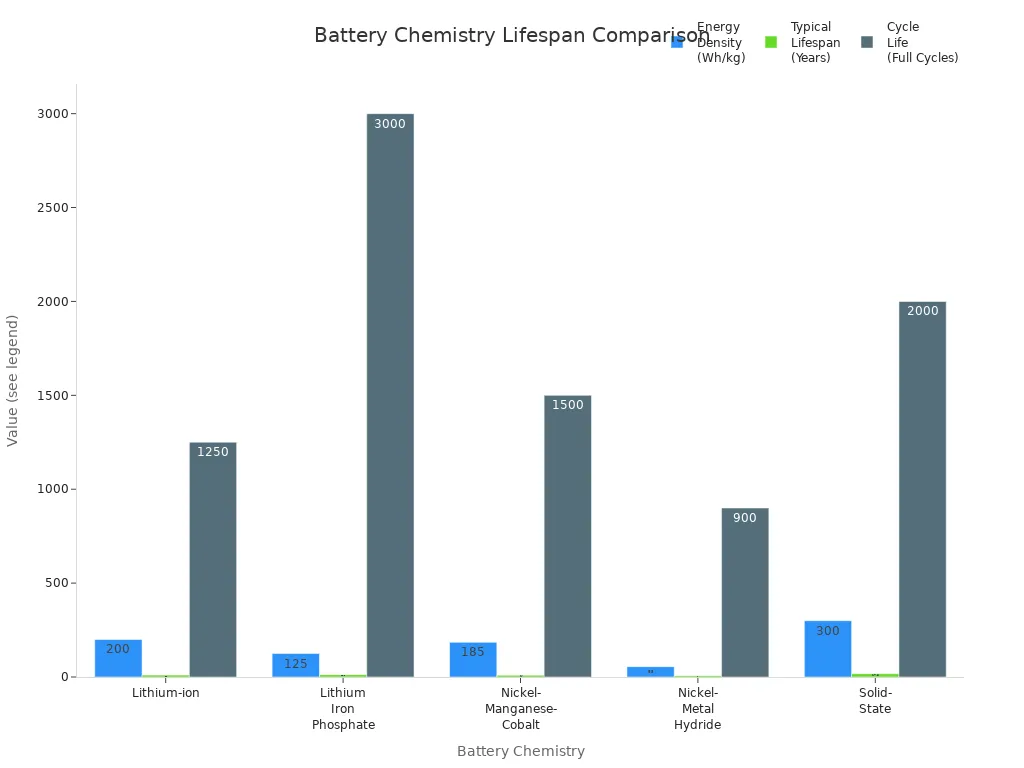
Different battery chemistries have different lifespans. For example, lithium-ion batteries usually last longer than nickel-metal hydride ones. Take a look at this table to see how chemistry affects battery lifespan and performance:
Battery Chemistry | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Typical Lifespan (Years) | Cycle Life (Full Cycles) | Key Influencing Factors and Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Lithium-ion | 150 - 250 | 8 - 10 (up to 15+) | 1,000 - 1,500 | Sensitive to fast charging, temperature extremes; requires monitoring of state of health and charge. |
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) | 90 - 160 | 10 - 15 | 2,000 - 4,000 | High safety and durability; less efficient in cold climates; benefits from moderate operating temperatures. |
Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC) | 150 - 220 | 8 - 10 | 1,000 - 2,000 | Balanced energy and lifespan; sensitive to heat and fast charging; thermal management critical. |
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) | 40 - 70 | 6 - 8 | 800 - 1,000 | Lower energy density; prone to memory effect; robust but largely outdated. |
Solid-State (Emerging) | >300 | 15 - 20 (projected) | >2,000 | High energy density and safety; still experimental with manufacturing challenges. |
Temperature Impact
Temperature plays a huge role in battery lifespan. If you store or use your battery in hot places, it will age faster. High temperatures speed up chemical reactions inside the battery, which leads to faster degradation and shorter lifespan. In fact, batteries in hot climates may last only about 40 months, while those in cooler places can last up to 55 months. On the other hand, cold weather slows down the battery and increases internal resistance, making it less efficient.
Try to keep your battery between 15°C and 35°C (59°F to 95°F) for the best results. This range helps slow down battery degradation and keeps your lithium battery lifespan longer.
Charge Cycles
Every time you charge and use your battery, you complete a cycle. The more cycles you go through, the more your battery degrades. Most lithium-ion batteries can handle 1,000 to 1,500 full cycles before you notice a big drop in performance. Partial charging, like keeping your battery between 20% and 80%, can help extend its lifespan.
You can get the most out of your battery by following good charging habits and avoiding extreme temperatures. This way, you protect your lithium battery lifespan and enjoy better battery performance for years.
Charging Tips for Extending Battery Life

You want your battery to last as long as possible. Good charging habits make a big difference. Let’s look at the best ways to keep your battery healthy and strong.
Avoid Overcharging
Leaving your device plugged in after it reaches 100% can hurt your battery health. Overcharging causes the battery to heat up. This heat can damage the inside of the battery, make it swell, or even cause it to fail. You might notice your device gets hot or the battery case looks puffy. These are signs of trouble.
Tip: Unplug your device once it’s fully charged. Many modern devices have automatic battery management systems that stop charging at 100%, but it’s still smart to disconnect when you can.
If you use a phone case, try removing it while charging. Cases can trap heat and make your battery even warmer. Keeping your battery cool helps prevent damage and supports battery lifetime extension.
Partial Charging
You don’t need to charge your battery all the way to 100% every time. In fact, charging between 20% and 80% is better for battery health. Partial charging puts less stress on the battery and helps it last longer. Frequent small charges are better than letting your battery drain all the way down and then charging it to full.
Lithium-ion batteries do not have a memory effect, so you can charge them whenever you want.
Keeping your battery in the mid-range (20%-80%) reduces wear and helps with battery performance.
Avoid deep discharges and full charges to keep your battery healthy.
Note: Research shows that batteries last longer when you avoid full discharges and favor partial charges. This simple habit can help with extending battery life.
Right Charger Use
Always use the charger that came with your device or one recommended by the manufacturer. Using the wrong charger can cause problems like overheating, undercharging, or even battery failure. Manufacturer-approved chargers have safety features that protect your battery, such as overcharge protection and temperature control.
Smart chargers adjust the charging rate to match your battery’s needs.
Charging at the right speed (not too fast) helps prevent heat and stress.
Avoid using cheap or unapproved chargers, as they can damage your battery and put your safety at risk.
Charging at room temperature is best. If your device feels hot or cold, let it reach room temperature before you plug it in. This helps keep your battery safe and improves battery performance.
Prevent Deep Discharge
Letting your battery drop to 0% can cause permanent damage. Deep discharges make the battery lose capacity and can even lead to complete failure. Most devices have a battery management system that warns you when the battery is low and shuts down before it gets too low.
Here’s a quick table to show the risks of deep discharge and how to avoid them:
Risk / Issue | What Happens | How to Prevent It |
|---|---|---|
Deep Discharge | Battery loses capacity or fails | Keep charge above 20%; charge before 0% |
Cell Imbalance | Some cells wear out faster | Use devices with battery management systems |
Increased Resistance | Battery becomes less efficient | Avoid deep discharges; charge regularly |
Capacity Loss | Battery holds less charge over time | Stay in the 20%-80% range; avoid full drains |
Reduced Cycle Life | Battery ages faster | Use partial charging; avoid deep discharges |
Reminder: Try to keep your battery above 20% and avoid letting it run all the way down. This habit helps with battery lifetime extension and keeps your device ready when you need it.
Quick Charging Habits Checklist
Charge between 20% and 80% for daily use.
Unplug your device when it’s fully charged.
Use slow charging when possible.
Remove your case during charging to prevent overheating.
Use only manufacturer-approved chargers.
Avoid charging in very hot or cold places.
Don’t let your battery drop to 0%.
By following these tips, you support proper charging and boost your battery health. These habits are easy to follow and make a big difference in how long your battery lasts.
Storage Tips for Battery Lifespan

Ideal Charge for Storage
When you plan to store your battery for a while, the charge level matters a lot. You should avoid storing batteries at 0% or 100%. For long-term storage, aim for a charge between 50% and 60%. If you only need short-term storage, keeping the battery at about 80% works well. This range helps reduce stress on the battery and keeps its lifespan longer. Here’s a quick table to help you remember the best storage guidelines for different battery types:
Battery Chemistry | Why It Matters | |
|---|---|---|
Lithium-ion | ~40% | Prevents deep discharge and slows capacity loss |
LiFePO4 | 50-60% | Reduces cell stress and chemical breakdown |
Nickel-based | Full or empty | High self-discharge, but capacity can recover with priming |
Lead acid | Fully charged | Stops sulfation and keeps capacity high |
Tip: Never store your battery at 0%. This can cause permanent damage and shorten battery lifespan.
Temperature and Humidity
Proper storage means more than just the right charge. You also need to think about temperature and humidity. Store your batteries in a cool, dry place. The best spot is around 59°F (15°C). High temperatures speed up battery aging and lower lifespan. Humidity can also hurt your battery by causing corrosion and faster capacity loss. Dry conditions slow down battery degradation and help your battery last longer.
Periodic Checks
Don’t forget to check your stored batteries every six months. If the charge drops below 20-30%, recharge it back to the safe range. This habit keeps your battery healthy and ready to use. For long-term storage, you can use a battery maintainer to keep the charge steady. Following these storage guidelines will help you get the most out of your battery storage and extend battery lifespan.
Safe Handling and Use
Physical Care
You can keep your battery safe and working longer with a few simple habits. Always follow the instructions from the manufacturer. Use only approved chargers and never leave your battery charging without watching it. If you notice a strange smell, heat, or swelling, unplug the battery right away. These signs mean something is wrong. For extra safety, use protective pouches like Lipo Guard bags when charging or storing your battery. If you have a lot of batteries, ask a safety expert for advice. Good battery care starts with these steps and helps prevent accidents.
Tip: Charge your battery only in places that the manufacturer recommends. This keeps you and your devices safe.
Avoid Moisture
Moisture is one of the biggest threats to battery safety and performance. High humidity can cause metal parts to rust and may lead to short circuits. When water gets inside, the battery can lose power faster and even become dangerous. You should keep your batteries in a place where the air is dry but not too dry. The best humidity level is between 30% and 50%. Using a dehumidifier or small packets that absorb water can help. This simple routine maintenance step protects your battery and keeps it working well.
Proper Containers
Choosing the right container is a big part of optimal battery care. Store lead acid and nickel cadmium batteries in strong, non-metal containers. Use plastic straps and wrap to keep them from moving. Never use metal restraints, as they can cause short circuits. For lithium-ion batteries, put each one in a clear plastic bag and cover the ends with tape. Fireproof containers made for batteries add another layer of safety. These steps make battery maintenance easier and safer for everyone.
Quick Reference Checklist
Daily Battery Tips
You want your battery to last longer and work better every day. Here’s a simple checklist to help you keep your battery in top shape:
Use the correct charger for your device. This helps prevent overheating and damage.
Keep your battery charge between 20% and 80%. Avoid letting it drop to 0% or stay at 100% for too long.
Unplug your device once it’s fully charged. Don’t leave it charging overnight.
Handle your battery with care. Try not to drop or bend it.
Check your battery for leaks, swelling, or corrosion. Clean the terminals if you see dirt.
Avoid deep discharges. Recharge before your battery gets too low.
Use your battery regularly. This keeps it active and healthy.
Replace your battery if it stops holding a charge or shows signs of damage.
Tip: Charging slowly is better for your battery than using fast charging all the time.
Long-Term Storage Tips
If you need to store your battery for a while, follow these steps to keep it safe and ready to use:
Store your battery in a cool, dry place. Aim for a temperature between 59°F and 77°F.
Keep the battery at about 40-60% charge during storage. This helps prevent capacity loss.
Avoid storing batteries near heat sources, water, or in humid places.
Use non-conductive containers or protective covers to prevent short circuits.
Label your batteries with the date and last charge. This makes it easy to track their condition.
Every three months, check your battery and recharge if needed.
Keep batteries away from flammable materials and make sure there is good airflow.
Note: Regular checks and proper storage can make your battery last much longer.
You can boost battery life with simple battery maintenance habits. Regular maintenance means fewer failures, better safety, and more savings. Remember, small changes—like checking charge levels and storing batteries right—make a big difference. Start these habits today and enjoy reliable power for years to come!
FAQ
How often should you check your battery for damage?
You should check your battery every month. Look for leaks, swelling, or dirt. Catching problems early keeps your devices safe.
Can you leave your device plugged in overnight?
It’s best not to leave your device charging overnight. Unplug it when it’s full to avoid overheating and help your battery last longer.
What should you do if your battery gets hot while charging?
Stop charging right away.
Let your device cool down.
Try charging in a cooler spot next time.